Penumbra has designed the Indigo System CAT RX device to make use of mechanical power aspiration to remove thrombus in the coronaries
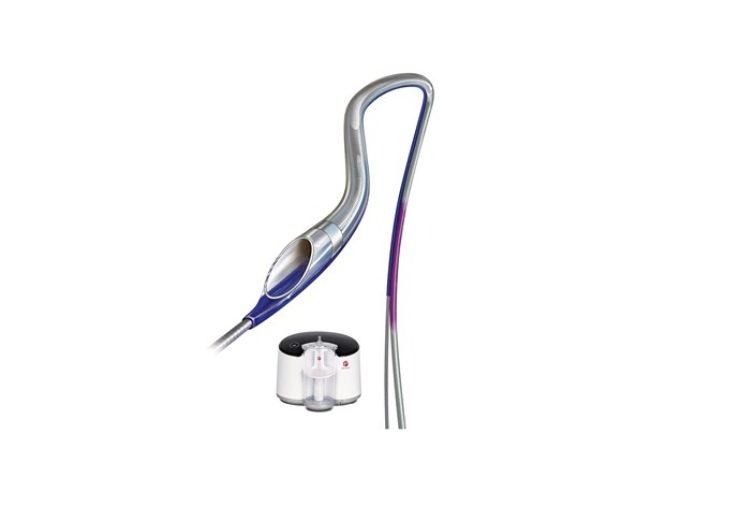
Image: Indigo System CAT RX Aspiration Catheter and Penumbra ENGINE. Photo: Courtesy of Business Wire.
Penumbra, a US-based provider of advanced therapies, has enrolled the first patient into the CHEETAH clinical study, designed to evaluate the safety and performance of the Indigo System with CAT RX Aspiration Catheter in the coronary vessels.
The healthcare firm said that the Indigo CAT RX Aspiration Catheters and Indigo Separator 4 are introduced in 2018, as part of the Indigo Aspiration System, and are indicated for the removal of fresh, soft emboli and thrombi from vessels in the coronary and peripheral vasculature.
Manatee Memorial Hospital cardiac catheterization laboratory director and national principal investigator S Jay Mathews said: “Penumbra has adapted over 10 years of neuro thrombectomy experience to address the limitations of traditional manual aspiration for the coronaries by development of the Indigo System CAT RX device.
“This significant upgrade in innovation from syringe-based aspiration to mechanical power aspiration coupled with highly trackable catheter technology has enabled us to improve our door to reperfusion times and thereby to improve patient care.”
Indigo System CAT RX device deploys mechanical power to remove thrombus in the coronaries
Penumbra has designed the Indigo System CAT RX device to make use of mechanical power aspiration to remove thrombus in the coronaries.
The company said that its Indigo CAT RX is a rapid exchange catheter intended for maximised clot removal using its large aspiration lumen, and offers advanced trackability and deliverability through seven material transitions and a proximal laser cut hypotube.
The post-market study CHEETAH is planned to enrol up to 400 patients with coronary thrombus and who are referred for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) from up to 25 US centres.
The primary study endpoint is a composition of cardiovascular (CV) death, recurrent myocardial infarction (MI), cardiogenic shock or new or worsening New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class IV heart failure within 30 days.
The secondary endpoints include final TIMI flow grade, final TIMI thrombus grade, and safety assessments at six months.
Washington University School of Medicine cardiac catheterization laboratory director Jasvindar Singh said: “Just like the IMS-III trial for ischemic stroke, the TOTAL trial highlighted that new therapies are needed to improve the outcomes of these patients with high thrombus burden.
“The CHEETAH study is the first step toward making coronary mechanical thrombectomy standard of care for high thrombus burden patients. We expect this study to refine our technique of thrombus aspiration and better understand the utilization of CAT RX for patients with high thrombus burden.”
