UK firm Smith & Nephew is in 'a strong position' to infiltrate the robotics surgery market with its new CORI platform, according to GlobalData
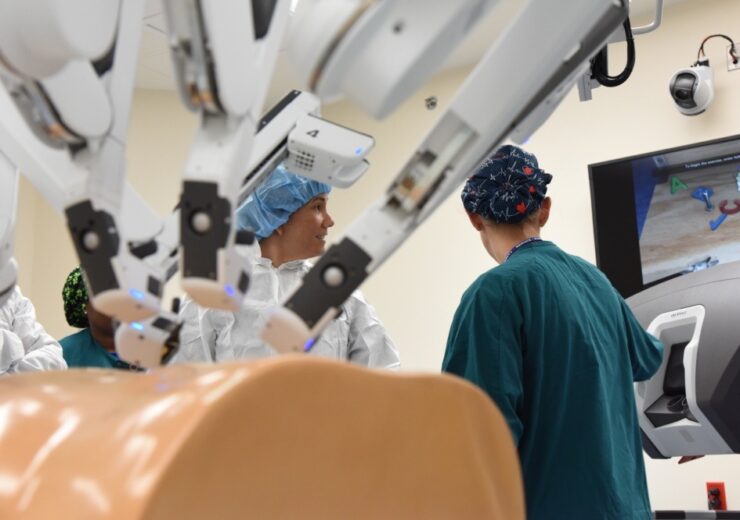
The robotics surgery market is currently being led by US firm Intuitive Surgical (Credit: 81st Training Wing Public Affairs)
Smith & Nephew is set to become a “key player” in the robotics surgery market after launching its CORI Surgical System, says an analyst.
The UK-based medical equipment manufacturer’s new handheld platform, which is used in knee arthroplasty procedures, puts it in a strong position to infiltrate this market, according to analytics firm GlobalData.
The small and portable “new generation” CORI Surgical System has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and was released alongside Smith & Nephew’s Real Intelligence brand of enabling technologies earlier this month.
Aliyah Farouk, medical device analyst at GlobalData, said: “GlobalData expects Smith & Nephew to be a key player in the robotics surgery market with the launch of its new, unique robotics platform.
“The key to market domination in this sector is typically product innovation and Smith & Nephew’s design sets it apart from competitors, placing the company in a strong position to infiltrate the market.
“The robotics surgery market, which is forecast to be worth $10bn in 2028 according to GlobalData, is currently led by Intuitive Surgical.”
The robotics surgery market
While US firm Intuitive Surgical currently leads the robotics surgery market, it also recently reported a sharp decrease in profits during the second quarter of 2020.
This has largely been attributed to the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, as shipping of the company’s da Vinci surgical devices dropped by 35% compared to Q2 last year, and worldwide procedures using these devices have also fallen by about 19%.
GlobalData estimates that Smith & Nephew will also feel the effects of Covid-19, and is “particularly exposed” to a downturn in sales within the orthopaedic and general surgery markets.
“Major orthopaedic devices manufacturers are increasing their research and development efforts within robotic surgical systems,” said Farouk.
“The landscape is rapidly changing with an increase in surgical procedures driving the installed base of surgical systems within hospital institutions.
“However, Covid-19 has led to the cancellation and postponement of elective procedures worldwide. In the US, the resumption of procedures has come to a halt in some areas as health systems deal with the new surge of Covid-19 patients.”
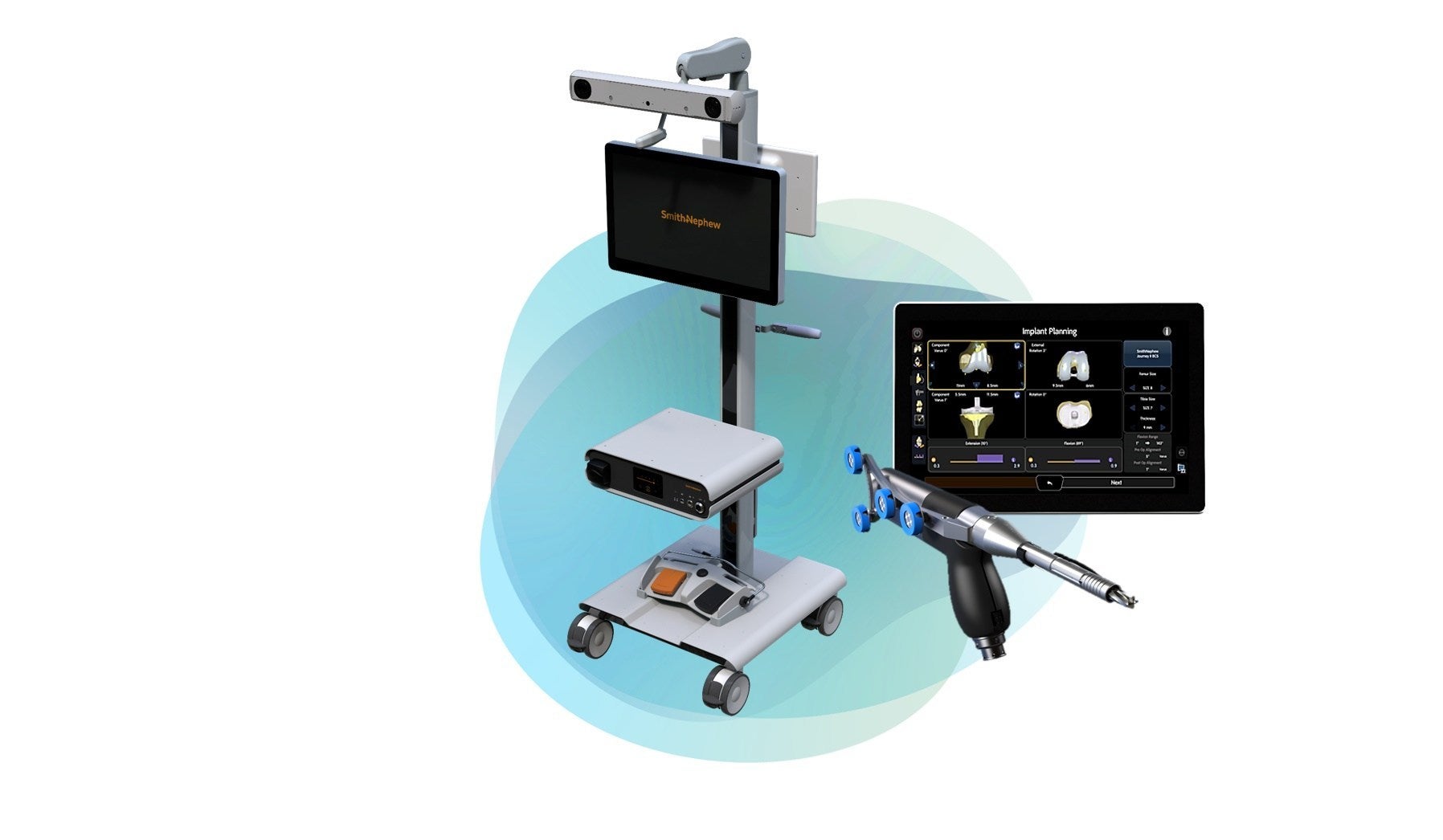
Smith & Nephew’s CORI Surgical System
Upon the release of its CORI Surgical System on 14 July, Smith & Nephew said the platform is small and portable, making it “ideal” for ambulatory surgical centres (ASCs) and outpatient surgery.
It is also designed for use in both unicompartmental knee arthroplasty — a procedure that relieves arthritis in one of the three main compartments of the knee — or total knee arthroplasty, which is more commonly referred to as total knee replacement surgery.
The CORI platform also includes new camera technology, which the company claims is more than four times faster, and offers more efficient cutting technology with twice the cutting volume, compared to another one of its surgical systems — the NAVIO platform.
Dr Jimmy Chow, a member of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons who specialises in hip and knee procedures, said: “The CORI Surgical System is truly next-generation robotics.
“Its efficient handheld form factor is ideal for surgery centres, which is where the market is moving, and it just erases away bone with the new bone milling technique.
“The smart, intuitive software helps place and size the implant, as well as balance gaps based on patient-specific anatomy and disease state.”
