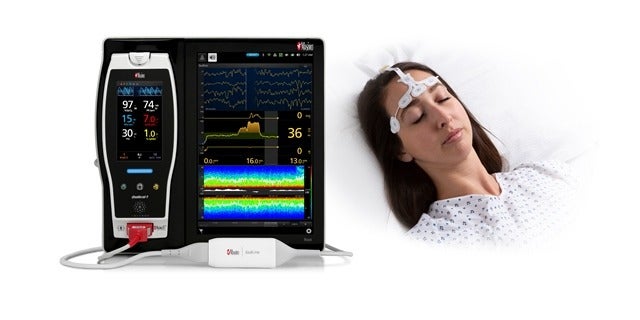
Masimo announced that the combination of two SedLine parameters, including patient state index (PSi) and suppression ratio (SR), has shown high predictability for mortality 180 days after cardiac arrest.
Dr Tae Youn Kim and colleagues at the Dongguk University College of Medicine and Yonsei University College of Medicine in Korea assessed the potential of two parameters offered by Masimo SedLine brain function monitoring for the prediction of neurological outcomes and long-term survival in post-cardiac arrest ICU patients.
Researchers used a multi-modal approach to assess the prognostic accuracy of the two Masimo SedLine parameters as predictors of neurological outcomes, both alone and in combination.
The team selected PSi as it is widely used in anesthesiology to determine the degree of procedural sedation, while SR was selected to estimate the percentage of EEG suppression. PSi is derived from EEG.
Masimo recruited 103 adult patients between January 2017 and August 2020 who experienced a non-traumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and successfully resuscitated after CPR. They were given targeted temperature management during their ICU stay.
Masimo SedLine was used to continuously monitor PSi and SR immediately after ICU admission until 24 hours after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Both parameters have been recorded at one hour intervals
Pittsburgh Brain Stem Score (PBSS) and Cerebral Performance Category (CPC) were used to categorise the neurological outcomes.
According to the company, the researchers noticed that using either PSi or SR alone had good predictability for poor neurological outcome and the combination of low PSi and SR had high predictability for mortality 180 days after cardiac arrest.
The researchers concluded that PSi and SR are good predictors for early neuro-prognostication in post-cardiac arrest patients, said the company.
The SedLine brain function monitoring system secured approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in January 2018.
Featuring an advanced signal processing engine, the system is designed to provide clinicians with a complete picture of the brain.






